IoT Gateway Solutions play a pivotal role in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem by acting as the bridge between IoT devices and cloud services or centralized data management systems. These gateways collect, process, and transmit data from multiple connected devices, ensuring seamless communication and operational efficiency. However, one of the critical challenges faced in IoT deployments is data loss during transmission or processing within the IoT gateway layer. Data loss can severely impact decision-making, automation, and analytics, leading to faulty operations and reduced system reliability.
In this blog, we will explore the common causes of data loss in IoT Gateway Solutions, methods for diagnosing these issues, and best practices to effectively fix and prevent data loss to ensure robust IoT operations.
What is Data Loss in IoT Gateway Solutions?
Data loss in IoT Gateway Solutions refers to the failure of transmitting or recording complete and accurate data from IoT devices to the backend systems. This can happen due to packet drops, buffer overflows, network interruptions, firmware bugs, or incorrect handling of data protocols. Since IoT Gateways are responsible for aggregating data from numerous sensors and devices, any loss at this stage can distort the overall data picture.
Common Causes of Data Loss
1. Network Instability: Network instability occurs when the connection between IoT gateways and the network (such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or cellular) experiences frequent disruptions, fluctuating signal strength, or intermittent outages. This instability can cause data packets to be lost or delayed, resulting in incomplete or missing data transmission between devices and cloud systems.
2. Buffer Overflows: Buffer overflow happens when an IoT gateway’s internal memory or temporary storage area (buffer) becomes full because it is receiving more data than it can process or transmit in real time. When the buffer exceeds its capacity, new incoming data packets may be discarded or dropped, causing data loss.
3. Protocol Mismatches and Incompatibility: Protocol mismatches and incompatibility arise when the communication standards or protocols used by IoT devices and gateways—such as MQTT, CoAP, or HTTP—are not properly aligned or supported. This misalignment can lead to errors in interpreting, parsing, or transmitting data, resulting in communication failures and data loss.
4. Firmware and Software Bugs: Firmware and software bugs refer to errors or flaws in the gateway’s embedded software (firmware) or the IoT platform applications that manage data flow. These bugs can cause malfunctions such as crashes, incorrect data handling, or processing errors, which may lead to loss or corruption of data.
5. Power Failures: Power failures are sudden interruptions or outages in the electrical supply to the IoT gateway. Without adequate backup power systems, these interruptions can cause the gateway to shut down abruptly, potentially losing any unsaved or in-transit data.
6. Data Corruption: Data corruption occurs when the integrity of data is compromised due to factors like electromagnetic interference, faulty hardware, or transmission errors. Corrupted data may be incomplete, altered, or unreadable, rendering it unusable for analysis or decision-making.
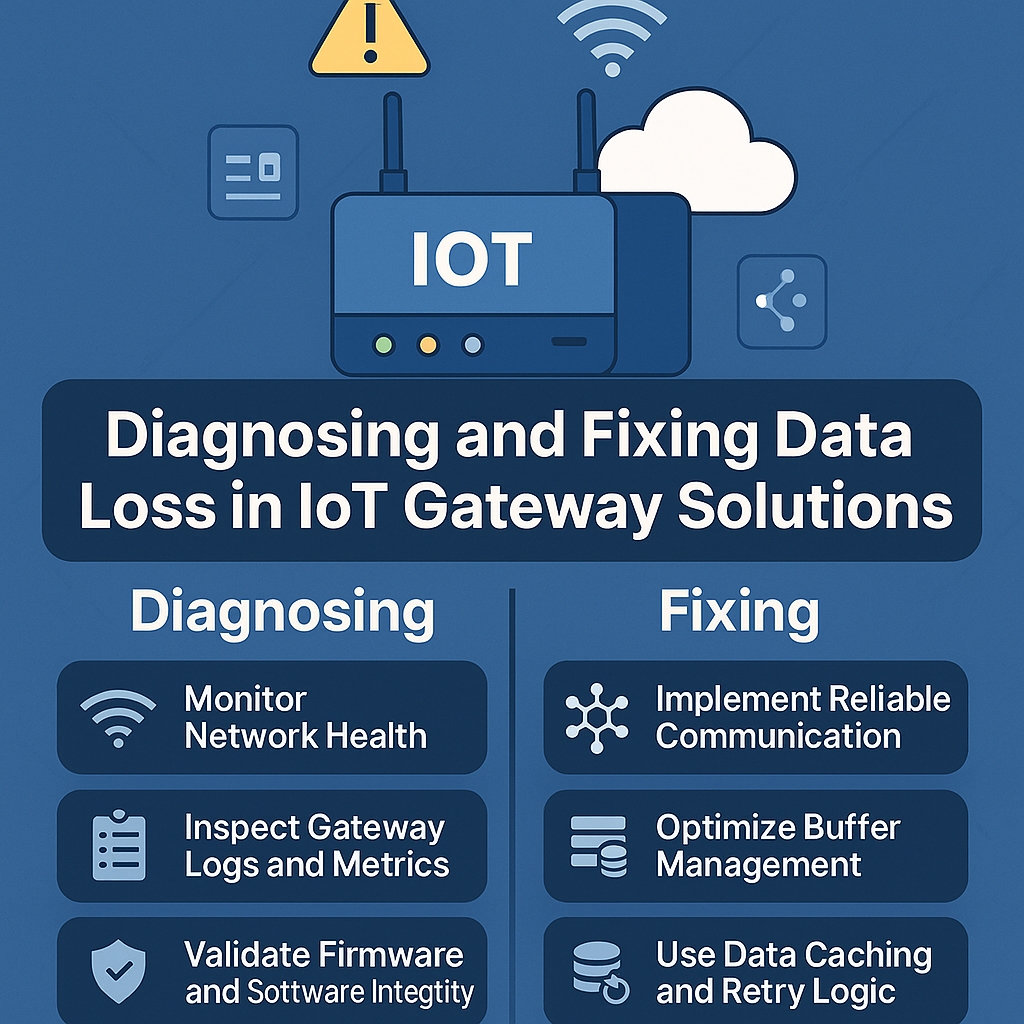
Diagnosing Data Loss in IoT Gateway Solutions
Step 1: Monitor Network Health
Use network monitoring tools to track latency, packet loss, and jitter on the gateway’s connection. Analyze logs to identify periods of disconnection.
Step 2: Inspect Gateway Logs and Metrics
Most IoT Gateway Solutions provide logs on message queues, buffer status, error codes, and transmission success rates. Scrutinize these logs for errors related to data drops or transmission failures.
Step 3: Validate Firmware and Software Integrity
Check for recent updates or known bugs. Rollback or patch firmware versions if issues are identified.
Step 4: Test Data Throughput and Buffer Capacity
Simulate high data volumes to observe buffer handling. Detect whether the gateway can sustain peak loads without dropping packets.
Step 5: Perform End-to-End Data Verification
Compare data at the device, gateway, and cloud levels to identify exactly where data loss occurs.
Fixing Data Loss: Best Practices and Solutions
a. Implement Reliable Communication Protocols
Use protocols with built-in quality of service (QoS) such as MQTT QoS 1 or 2 to guarantee message delivery.
b. Optimize Buffer Management
Increase buffer sizes and apply backpressure mechanisms to prevent overflow. Implement priority queues to handle critical data first.
c. Enhance Network Reliability
Deploy redundant network connections or use failover mechanisms to ensure continuous connectivity.
d. Regular Firmware and Software Updates
Keep gateway software updated to patch bugs and improve data handling capabilities.
e. Use Data Caching and Retry Logic
Incorporate local caching so that data is temporarily stored during network outages and retransmitted once the connection is restored.
f. Power Backup Solutions
Integrate UPS or battery backups for gateways in critical environments to avoid data loss due to power failures.
g. Data Validation and Error Correction
Implement checksum or hash-based validation to detect corrupted data and request retransmission.
Preventive Measures for Data Integrity
1. End-to-End Encryption: Protects data by encrypting it at the source and decrypting it only at the destination, ensuring data cannot be intercepted or altered during transmission.
2. Regular Audits: Involves periodic reviews of gateway and device logs to identify errors, unusual activity, or data inconsistencies early and address them promptly.
3. Network Quality of Service (QoS): Manages network traffic by prioritizing critical IoT data to minimize delays and packet loss, maintaining smooth and reliable communication.
4. Edge Processing: Processes and filters data on the IoT gateway itself, reducing the volume sent over the network and enabling faster detection of anomalies or errors.
5. Scalable Architecture: Builds IoT gateway solutions that can easily expand capacity to support growing numbers of devices and larger data volumes without degrading performance or causing data loss.
Conclusion
Data loss in IoT Gateway Solutions is a critical issue that can disrupt operations and degrade the quality of insights derived from IoT systems. By understanding the root causes and adopting a systematic approach to diagnose and fix these problems, organizations can ensure the reliability and accuracy of their IoT data pipelines. Incorporating robust protocols, optimizing hardware and software, and implementing fail-safes are essential steps toward maintaining data integrity and achieving successful IoT deployments.
FAQs
Q1: How can IoT Gateway Solutions handle intermittent network connectivity?
By using local caching, retry mechanisms, and failover networks, gateways can buffer data during outages and retransmit once connectivity is restored.
Q2: Are firmware updates important for preventing data loss?
Yes, firmware updates fix bugs and improve data handling performance, reducing the risk of data loss.
Q3: What role do communication protocols play in data loss?
Protocols with QoS features ensure message delivery and prevent data loss during transmission.
Q4: Can power failures cause permanent data loss in IoT gateways?
Yes, without proper power backup, unsaved data may be lost during outages.
Q5: How to monitor if data loss is happening in my IoT system?
Use monitoring tools to check network stability, analyze gateway logs, and verify data consistency across system layers.
