The Medical Simulation Market represents one of the most transformative advancements in modern healthcare education and training. It revolves around the use of advanced technologies, realistic models, and immersive learning platforms that replicate clinical scenarios for healthcare professionals. Unlike traditional teaching methods, medical simulation enables trainees to experience complex medical situations in a risk-free environment. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, this market has become a cornerstone in improving patient safety, clinical outcomes, and the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
Understanding the Concept
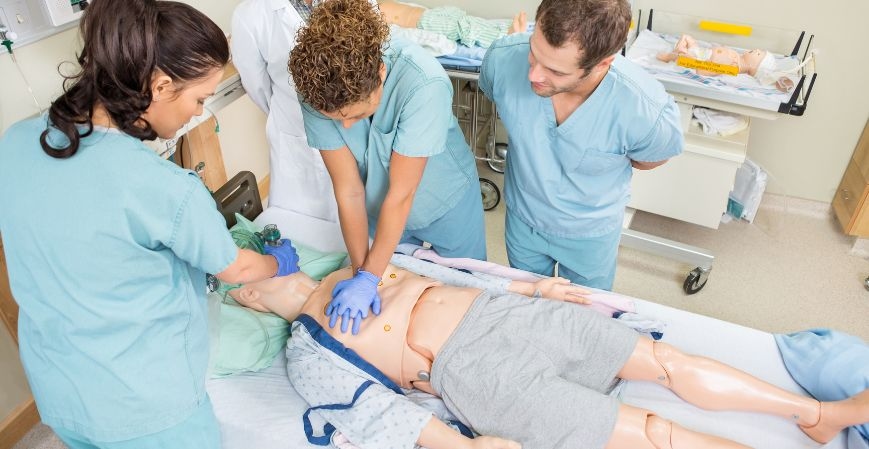
At its core, the medical simulation market encompasses a range of technologies and methodologies designed to replicate clinical practices. These include mannequin-based simulations, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), haptic feedback devices, and computer-based learning modules. High-fidelity simulators mimic human physiology, allowing trainees to perform procedures such as intubation, surgery, or resuscitation under realistic conditions.
Beyond physical simulators, software-driven simulation platforms offer interactive, scenario-based training that can be customized for specific medical disciplines—ranging from anesthesiology and emergency medicine to nursing and obstetrics. Additionally, simulation centers have become integral to medical schools and hospitals, enabling structured learning in environments that mirror operating rooms or intensive care units.
This convergence of advanced hardware, software, and clinical expertise defines the medical simulation ecosystem. It supports continuous professional development, reduces learning curves, and promotes competence before patient interaction.
The Problem It Solves
The medical field faces a consistent challenge: how to train healthcare professionals effectively without compromising patient safety. Traditional medical education often relies on classroom instruction and on-the-job training, where real patients may be involved in learning procedures. This approach can expose patients to unnecessary risk and limit the range of experiences trainees encounter.
The medical simulation market addresses these issues by providing a controlled, repeatable, and safe environment for skill development. It allows healthcare workers to make mistakes, learn from them, and repeat procedures until mastery is achieved—without endangering lives. Furthermore, simulation helps reduce medical errors, one of the leading causes of adverse outcomes in healthcare.
Another major problem it solves is the shortage of experienced trainers and the variability in clinical exposure across regions. Simulation-based learning ensures standardized training, meaning a trainee in one institution can receive the same quality of practice as another halfway across the world. This democratization of medical education is vital in improving the consistency and reliability of global healthcare standards.
Significance
The importance of the medical simulation market extends beyond education—it impacts patient care, healthcare operations, and policy-making. For healthcare providers, simulation-based training improves diagnostic accuracy, decision-making under pressure, and teamwork in multidisciplinary settings. Hospitals that integrate simulation programs often experience higher efficiency and reduced incidence of preventable errors.
For patients, the benefits translate into safer and more confident healthcare professionals who can manage complex cases more effectively. In addition, simulation supports evidence-based training, allowing clinical procedures to evolve in tandem with emerging technologies and treatments. Regulatory bodies and accreditation organizations are also increasingly emphasizing simulation as part of mandatory training requirements, reflecting its growing institutional significance.
Practical Applications
Today, the medical simulation market finds application across a wide spectrum of healthcare settings. Surgical simulation enables physicians to practice delicate procedures using realistic 3D anatomical models. Emergency response simulations train teams to handle trauma cases, cardiac arrests, and disaster scenarios with precision and coordination. In nursing education, simulation helps students build confidence in patient interaction, medication administration, and critical thinking.
Moreover, the use of virtual and augmented reality has expanded the possibilities of medical training. VR-based platforms immerse learners in dynamic clinical environments, enhancing their ability to assess, diagnose, and treat patients virtually. Simulation is also instrumental in interprofessional education, fostering collaboration between doctors, nurses, and technicians to improve communication and patient outcomes.
Pharmaceutical and medical device companies are increasingly adopting simulation technologies to train professionals on new tools or therapies. This ensures safe implementation and accelerates innovation adoption across the healthcare ecosystem.
Future Landscape
The future of the medical simulation market is set to be defined by digital integration, personalization, and remote accessibility. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are beginning to play a role in creating adaptive learning systems that assess performance and customize training accordingly. These intelligent platforms will help learners identify weaknesses and receive targeted feedback in real-time.
Cloud-based simulation and remote training solutions are also expected to gain traction, allowing healthcare professionals from different geographies to collaborate and train virtually. The merging of simulation data with clinical analytics could provide insights into skill gaps, improving workforce planning and competency tracking.
Ethical considerations, cost efficiency, and expanding access to low-resource regions will continue to drive innovation. As simulation technologies become more affordable and scalable, their adoption will likely extend to every level of medical education—from undergraduate studies to continuing professional development.
